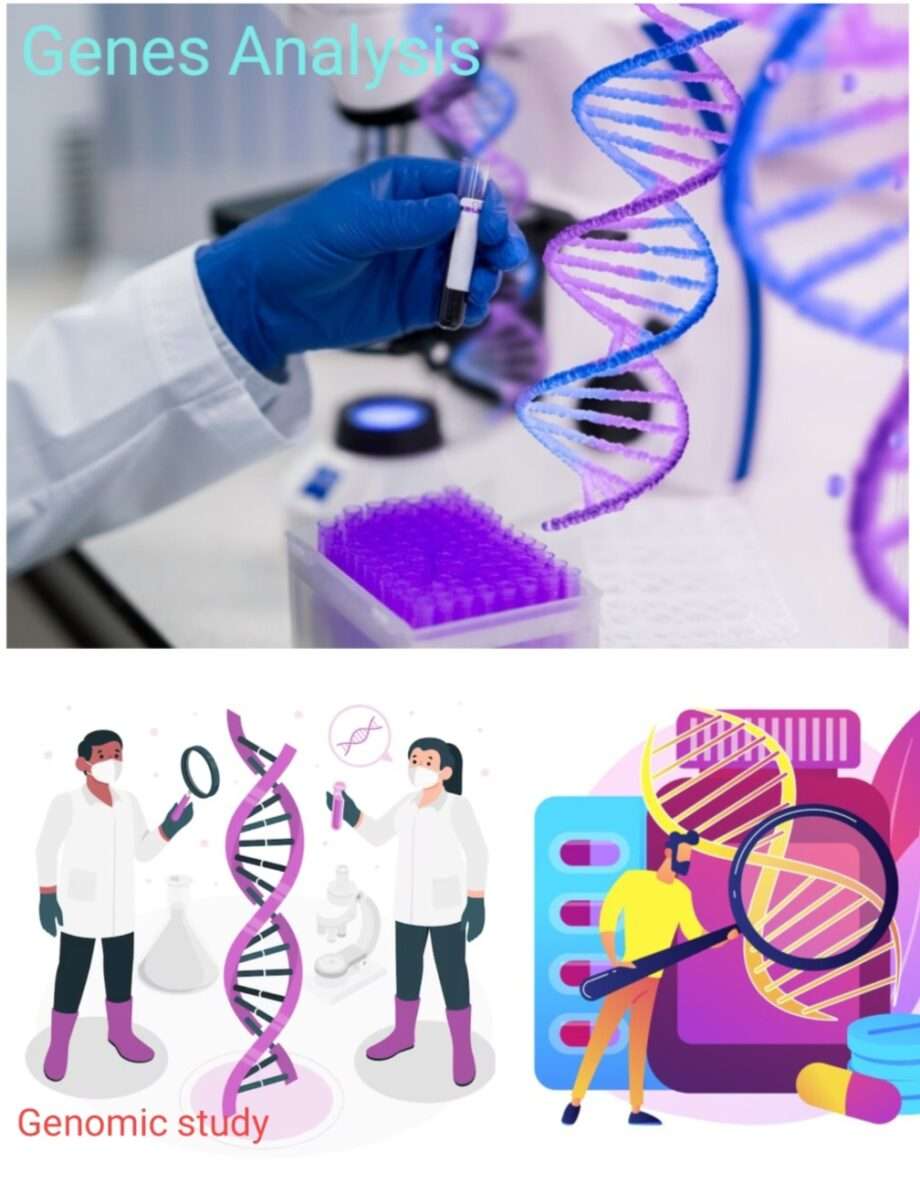
Treatment according to personal genes is based on the principle that no two individuals are the same in their genetic makeup. Each person possesses a unique genetic code, lifestyle choices, and environmental exposures that influence their health and response to treatments. With advancements in genomics, molecular diagnostics, data analytics, and personalized medicine, it is possible to optimize therapeutic strategies for maximum efficacy and minimal adverse effects. It comes under the domain of personalized treatment.
- Table of Content
- 1-Genomic profiling
- 2. Molecular profiling
- 3. Targeted Therapy
- 4. Genomic pharmacology
- 5. Prediction of risk factors and disease
- 6: Customized patient care
- 7. Pros and Cons of Personalized Medicine
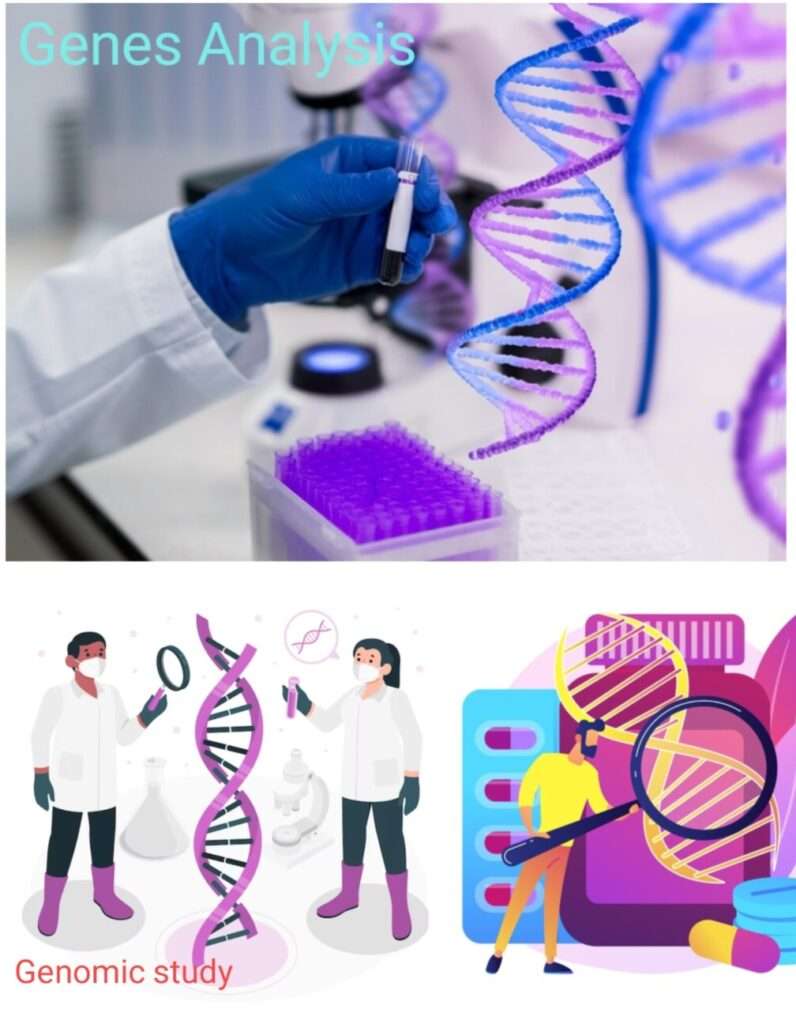
Genomics is the basis of personalized medicine. It is the study of an individual’s genetic makeup. With techniques such as DNA sequencing, scientists can identify genetic variations that increase their susceptibility to certain diseases or affect their response to medications.
2. Molecular profiling further increases this understanding by analyzing the molecular characteristics of diseases at a cellular level, allowing for tailored treatment approaches. The synthesis of these two, fields provides valuable insights into disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
3. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapeutics are one of the main uses of personalized medicine. These medications target particular molecular targets linked to those diseases, enabling a more focused and efficient recipe. Targeted medicines, as opposed to traditional treatments, can decrease side effects and enhance outcomes by matching therapies according to the unique genetic profile of each patient.
4. Genomic pharmacology
Pharmacogenomics tells, how a person’s genetic composition is affected and how they react to medications. It investigates the relationship between an individual’s genetic makeup and their response to drugs. It also investigates how genetic variations influence drug efficacy, toxicity, and metabolism. Healthcare professionals can assess pharmaceutical regimens to enhance outcomes and lower the risk of adverse responses by studying genes that impact drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity. There is a lot of potential for increasing patient safety and treatment outcomes with a customized genomic approach.
5. Prediction of risk factors and disease

Predictive diagnostics is another method of customized medicine that evaluates a person’s likelihood of contracting specific diseases. Healthcare professionals can determine whether a patient is at high risk for diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or cancer by using genetic testing and other predictive technologies. Proactive measures, including lifestyle changes or preventive medicine, can be implemented to minimize the risk.
The idea of patient-centered care is essential to individualized medicine. Healthcare specialists can effectively customize care plans to fit the needs of individual patients, their values, and their circumstances. which improves treatment compliance and produces better health outcomes
7. Pros and Cons of Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine has great potential, but it also encounters some obstacles, such as the high cost of genomic testing, concerns about data privacy, and the need for strong evidence to support its wider adoption. Ongoing developments in data science, technology, and healthcare delivery systems create optimistic scenarios. In the upcoming years, personalized and customized medicine should be available. Satish Tripathi sctri48